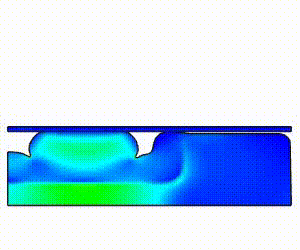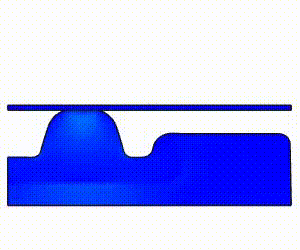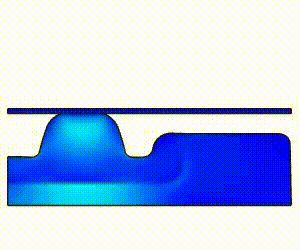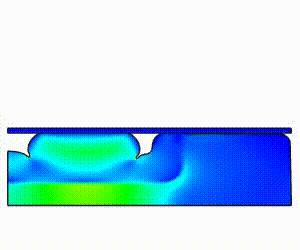
webFalcon : WEB Based FEA Solution
webFalcon is the web based FEA Solution based on framework developed by Sutra. This framework enables you to quickly develop web based CAE Applications. Sutra uses the same framework to develop design applications that can be implemented on the web at very low cost. Application does not need installation on all clients and can be used in the Browser.
webFalcon provides most of the features that of Falcon which is a Desktop Application. The application has complete Pre Processing, Analysis (Open Source Solvers) and Post Processing capabilities.
As it is hosted on a web server, common database of materials, tables from library are available to all users. All the solver execution is done on the server using batch queuing system. All the analysis data can also be shared by many users.
Overview
![]() 3D Geometry (STL) or 2D Geometry (DXF) data support
3D Geometry (STL) or 2D Geometry (DXF) data support
![]() Material library (Elastic/Hyper Elastic/Elastoplastic/Thermal/Non Linear/Temperature Dependent)
Material library (Elastic/Hyper Elastic/Elastoplastic/Thermal/Non Linear/Temperature Dependent)
![]() Non Linear Table definitions
Non Linear Table definitions
![]() Various Structural/Thermal Boundary condition definition on Geometric Model data
Various Structural/Thermal Boundary condition definition on Geometric Model data
![]() Complete 2D and 3D Auto mesh with Mesh Size control
Complete 2D and 3D Auto mesh with Mesh Size control
![]() Multiple analysis types [Static/Frequency/Heat Transfer]
Multiple analysis types [Static/Frequency/Heat Transfer]
![]() Interface to Open Source Solvers Calculix, Code-Aster
Interface to Open Source Solvers Calculix, Code-Aster
![]() Contour/Deformation Result display with Animation
Contour/Deformation Result display with Animation
![]() FEA Data Import/Export support
FEA Data Import/Export support
![]() Multilingual support (English/Japanese/Other: controlled by browser)
Multilingual support (English/Japanese/Other: controlled by browser)
![]() User access rights control
User access rights control
Typical Application Interaction Flow
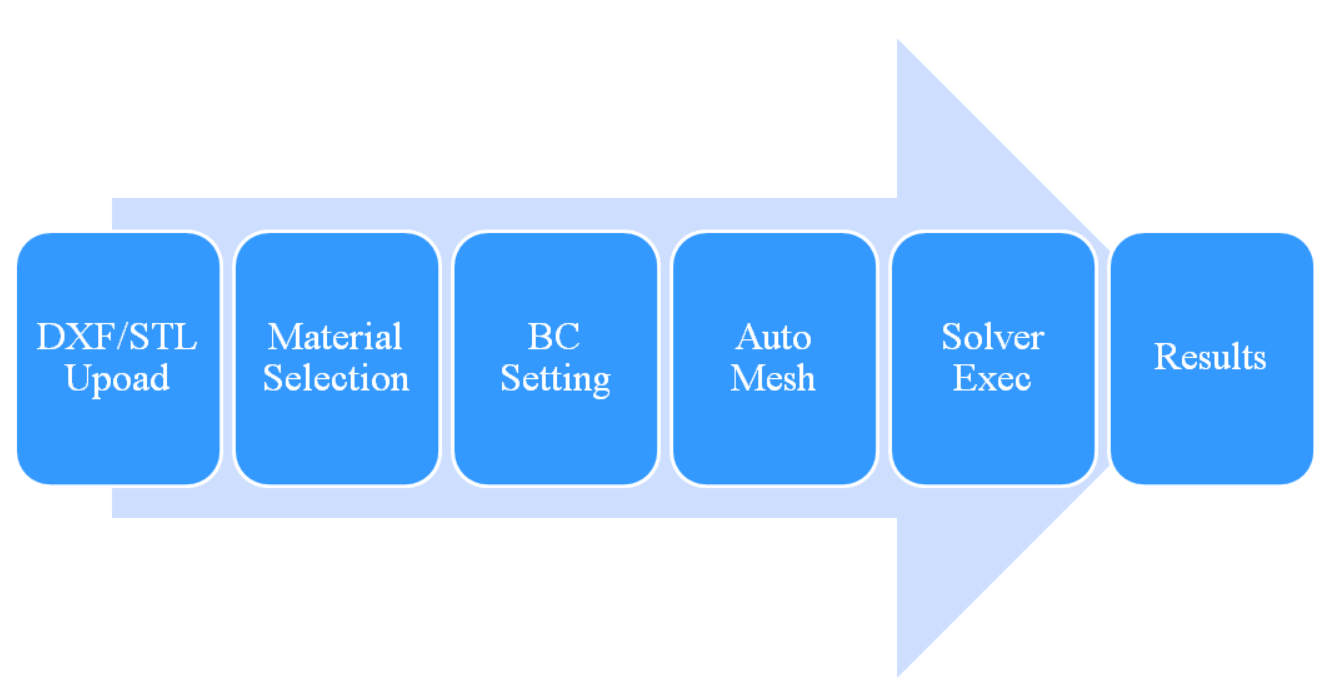 Guide to analysis processing with Wizard
Guide to analysis processing with Wizard
1. Steps for 2D Model Analysis:
2. Steps for 3D Model Analysis:
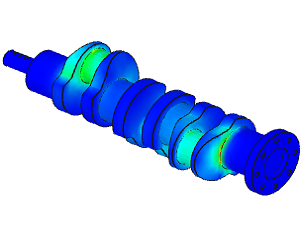
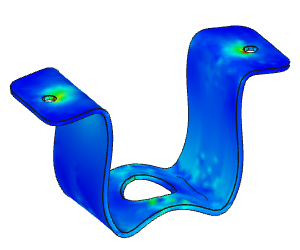
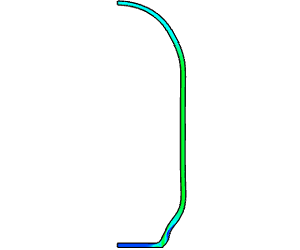
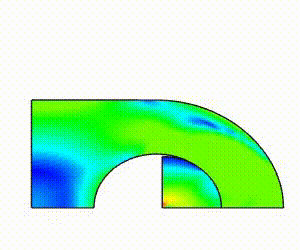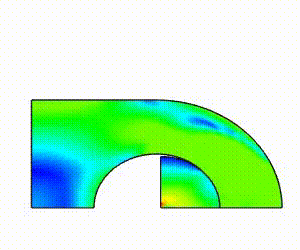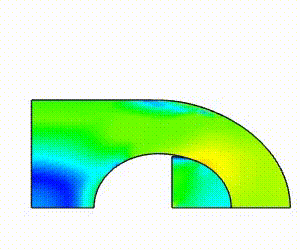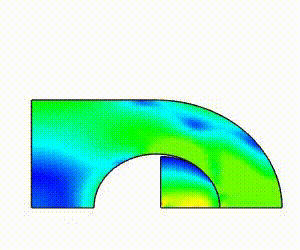
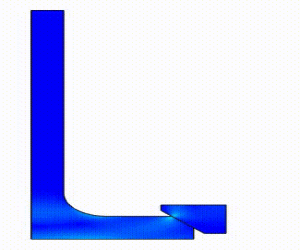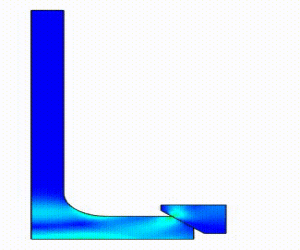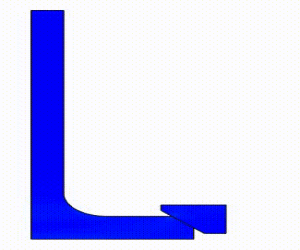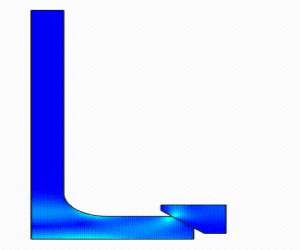
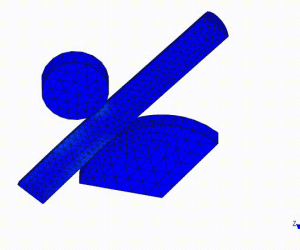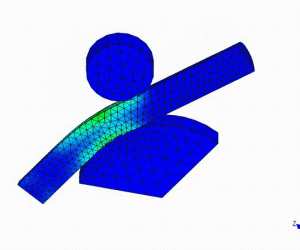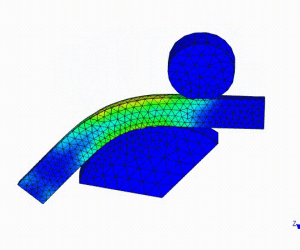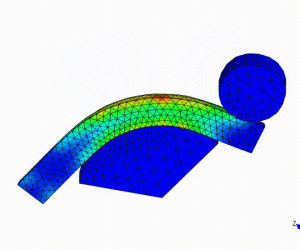
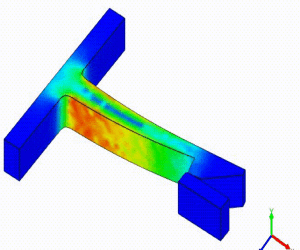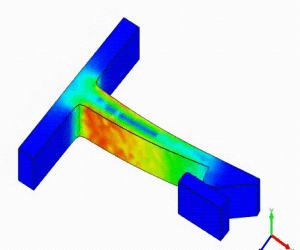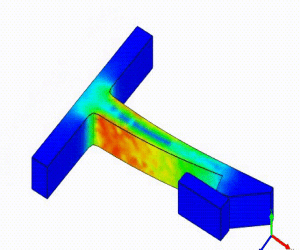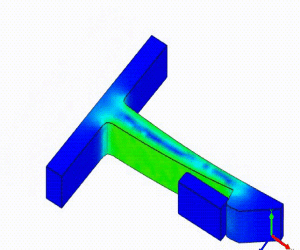
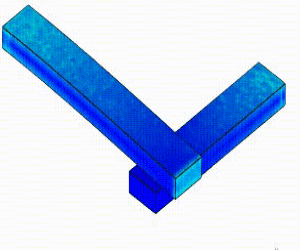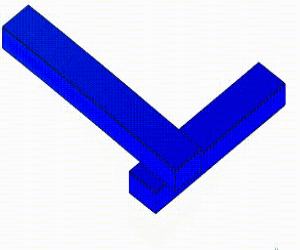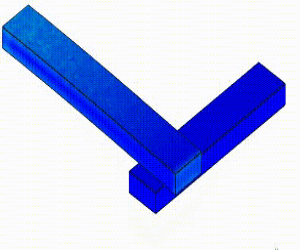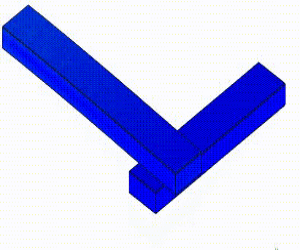
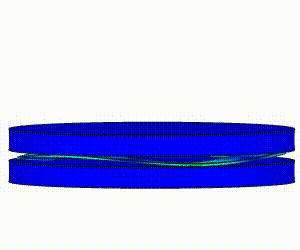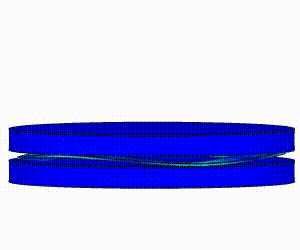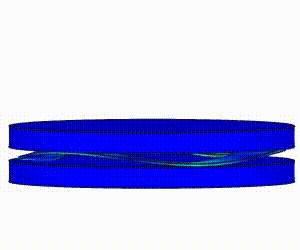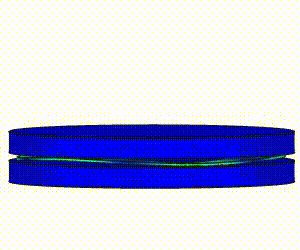
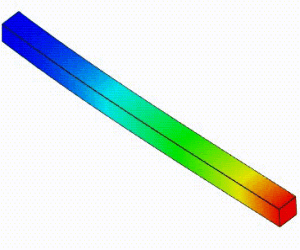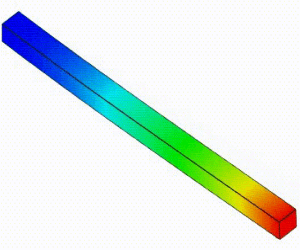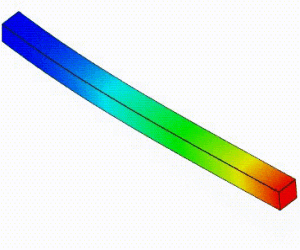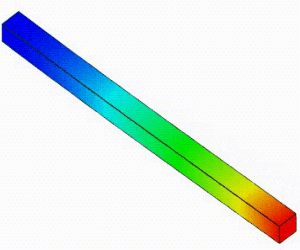
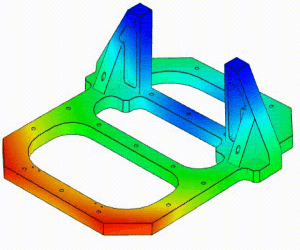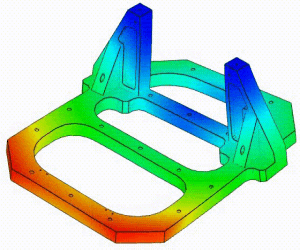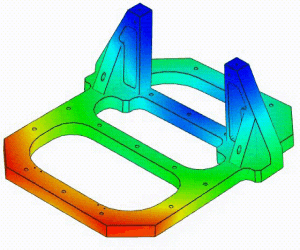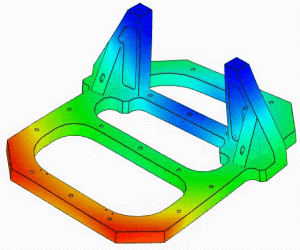
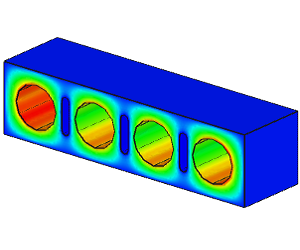
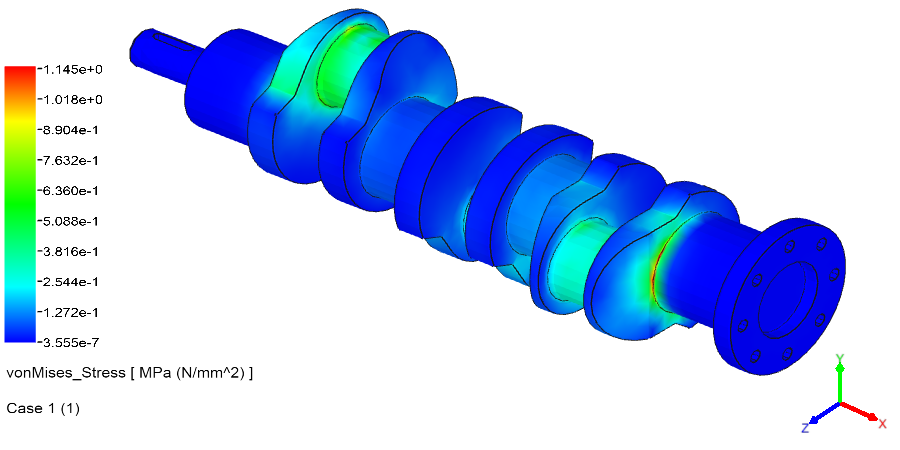
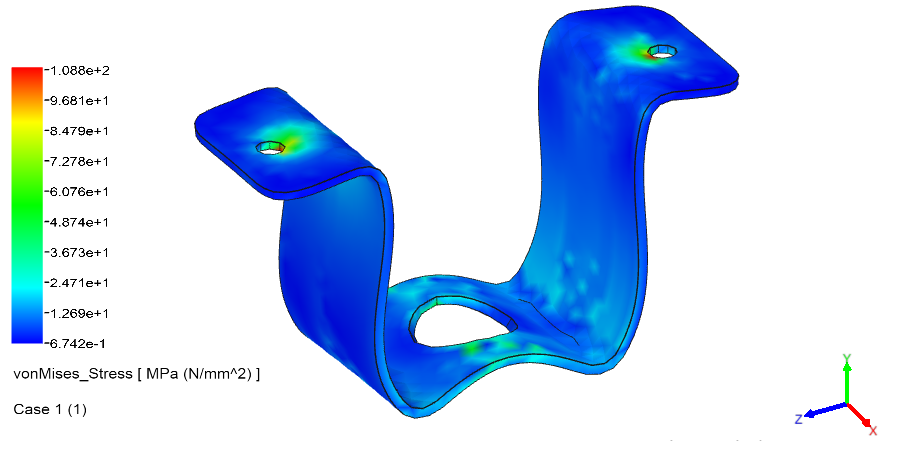
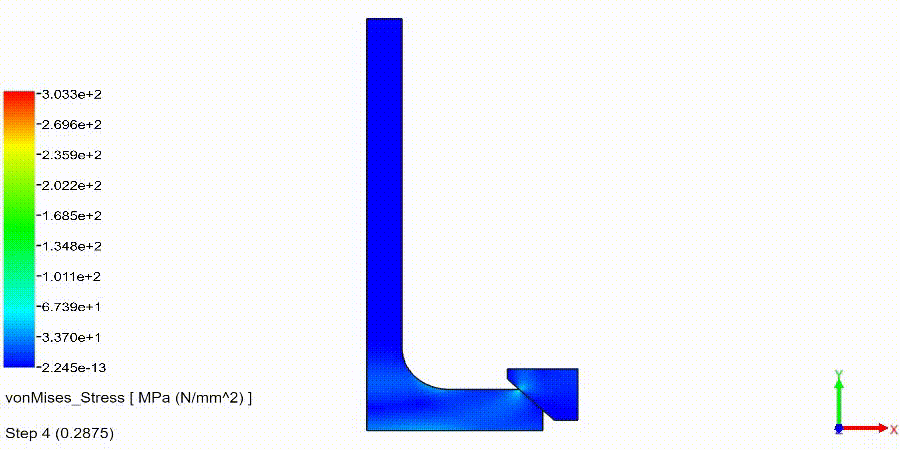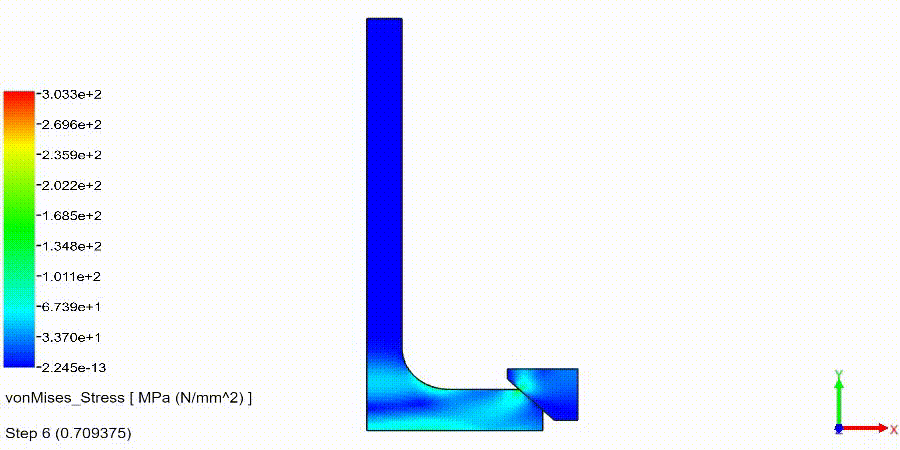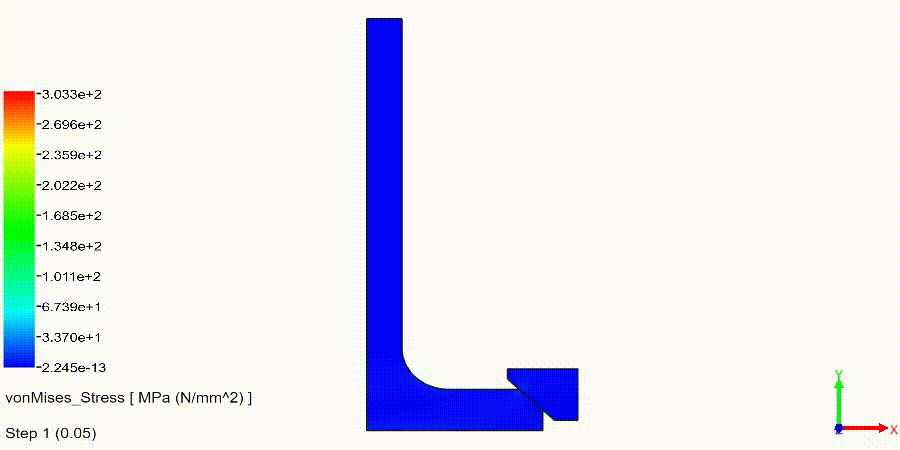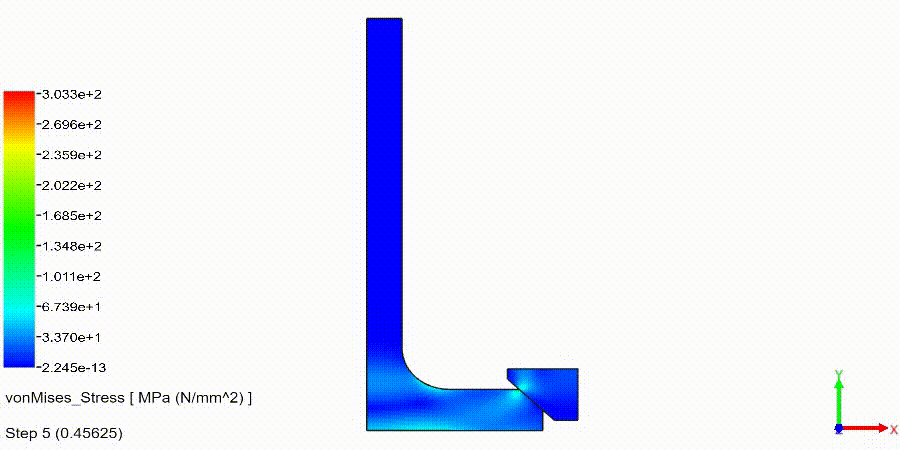
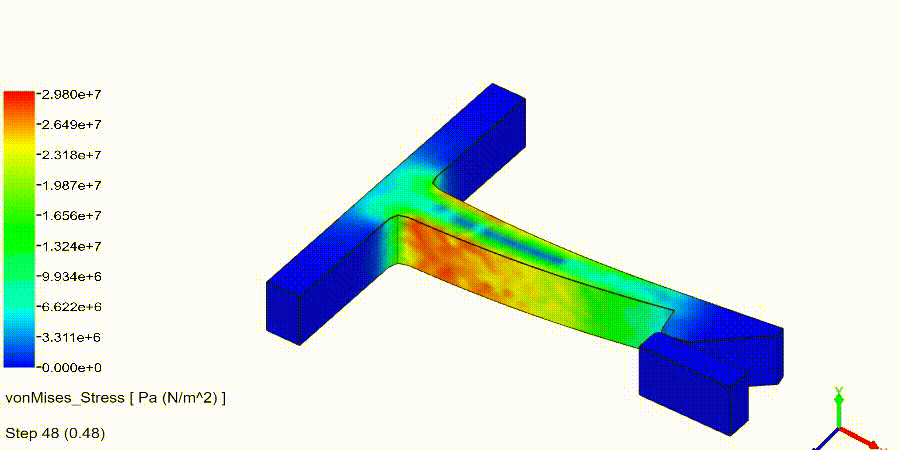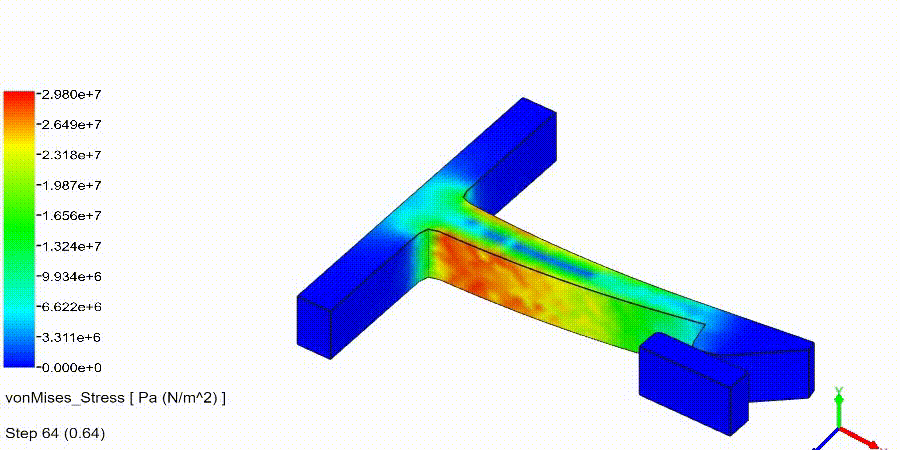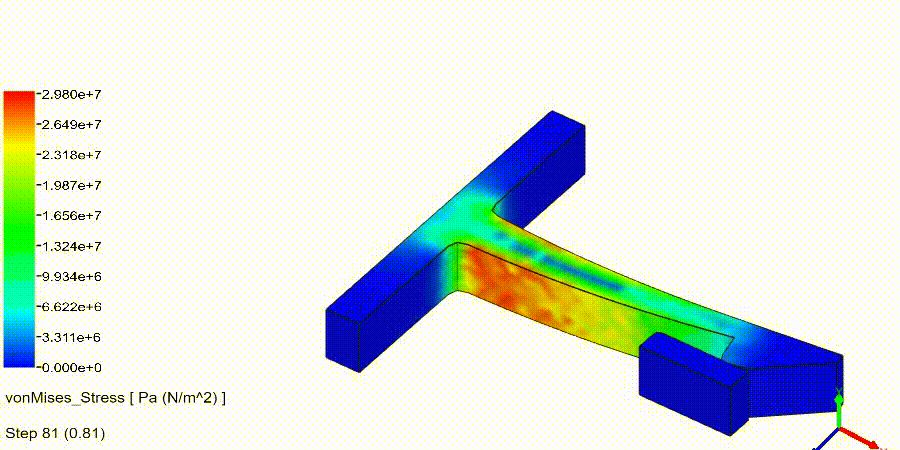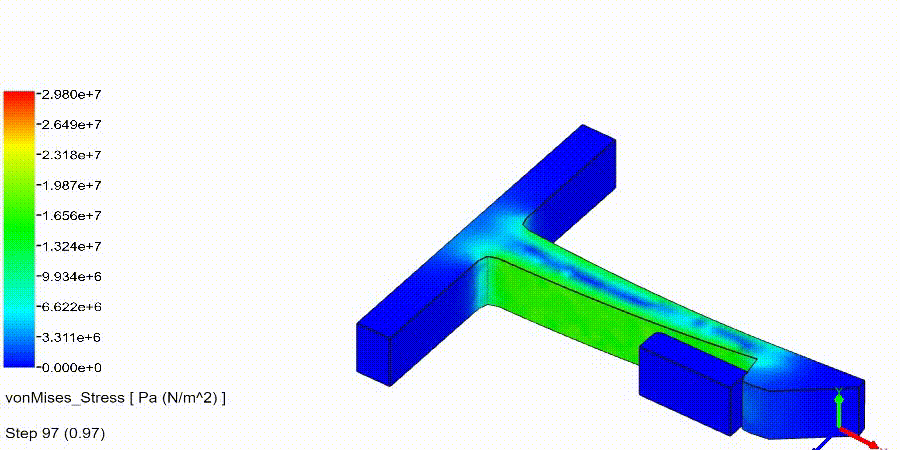
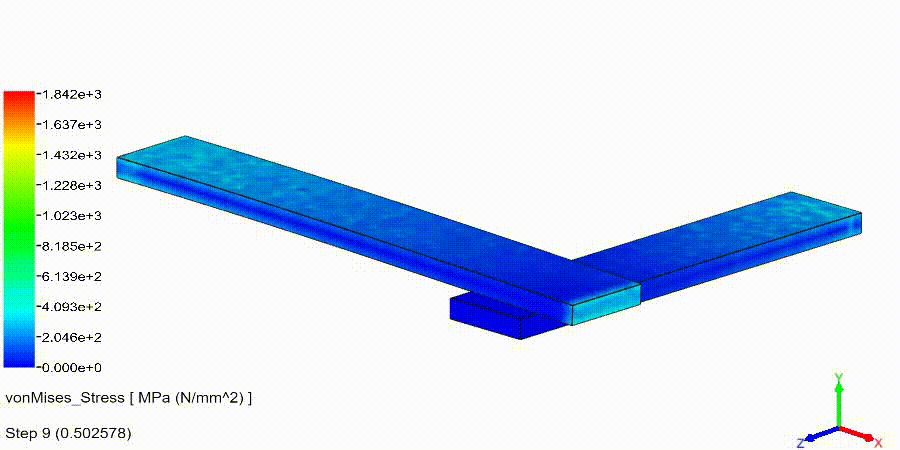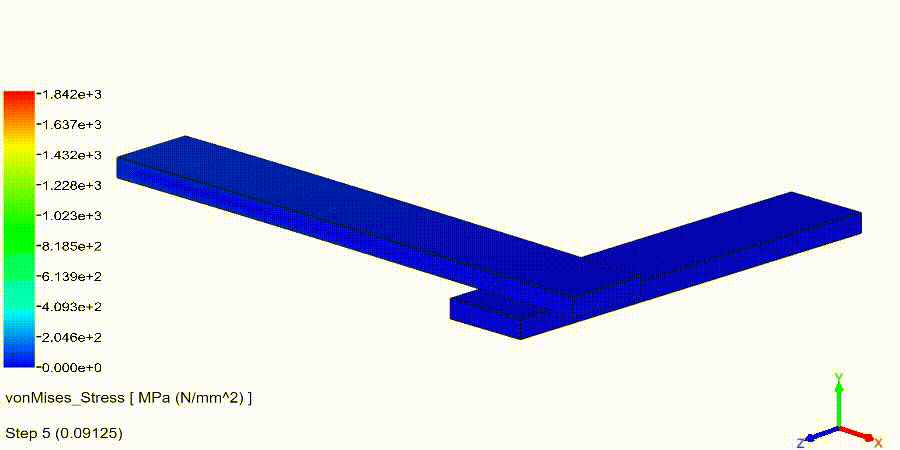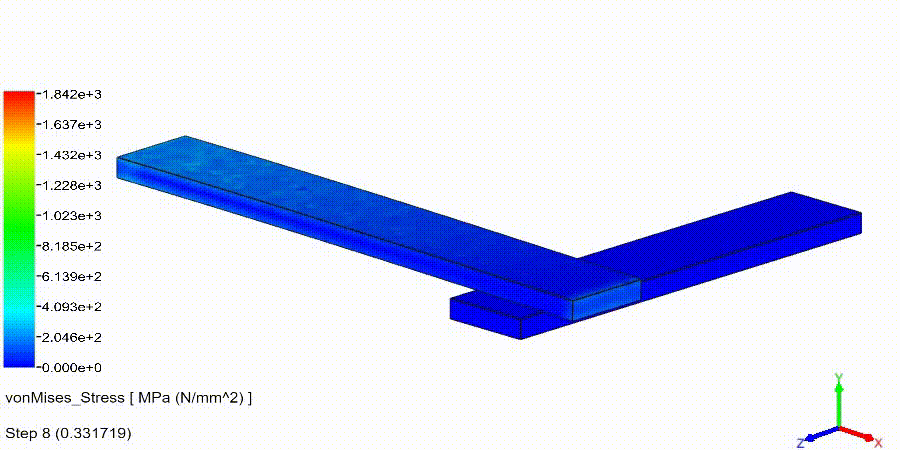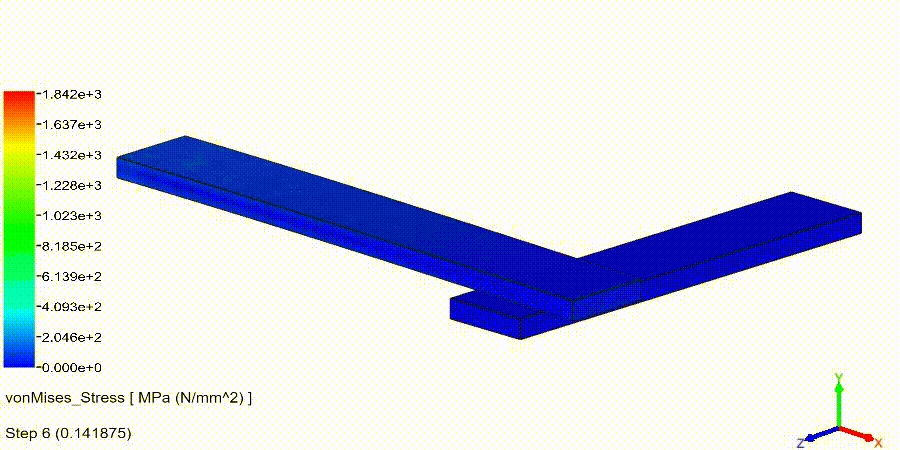
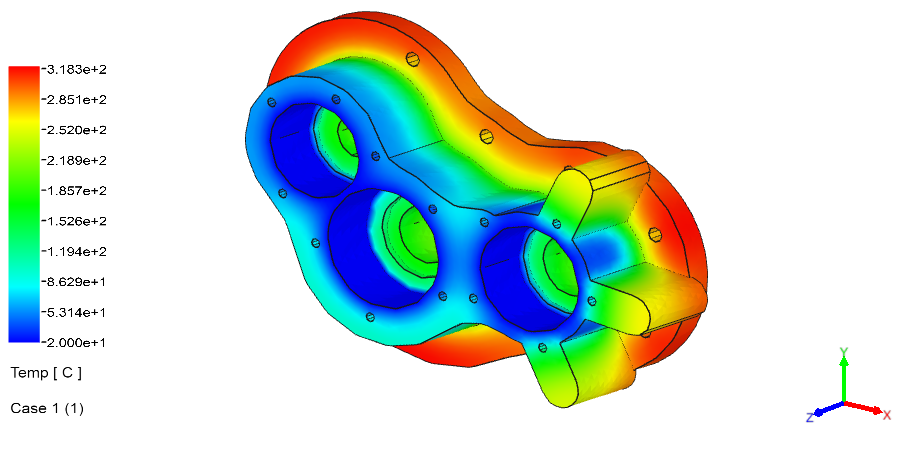
Linear Static Analysis Examples :
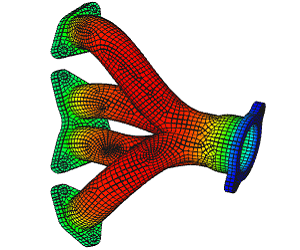
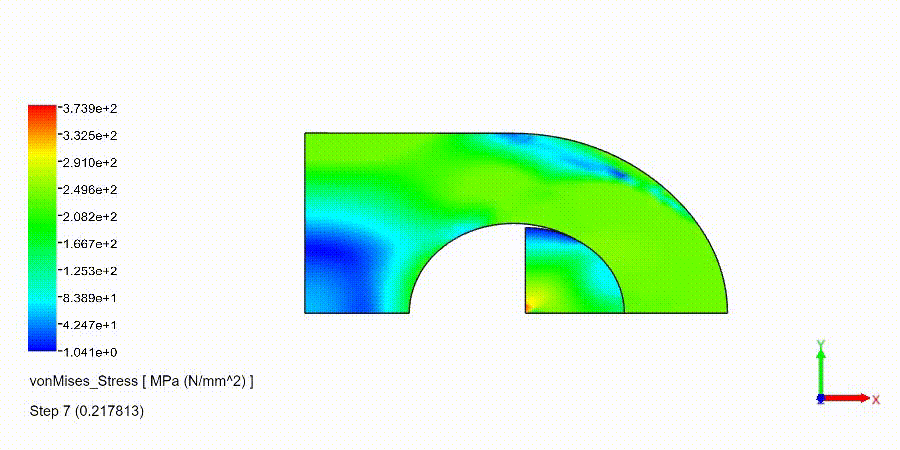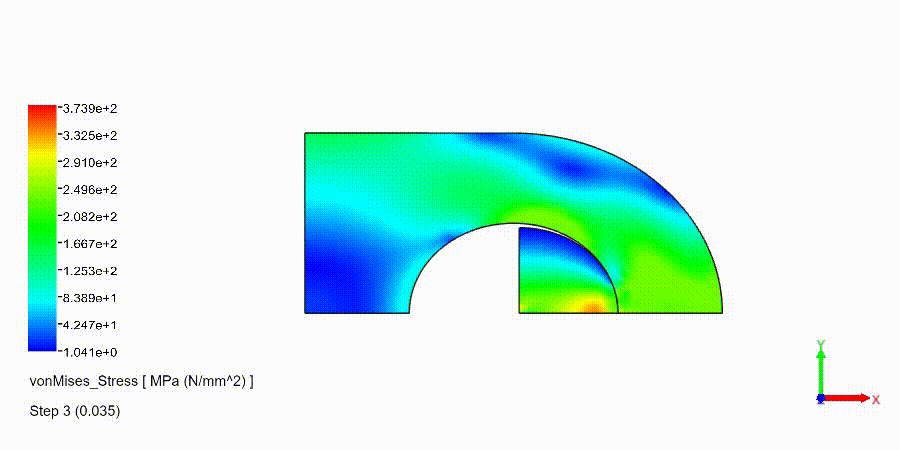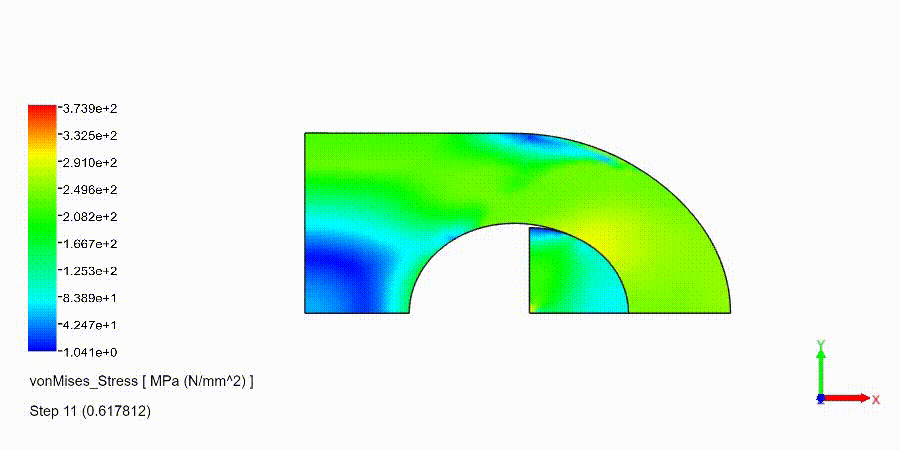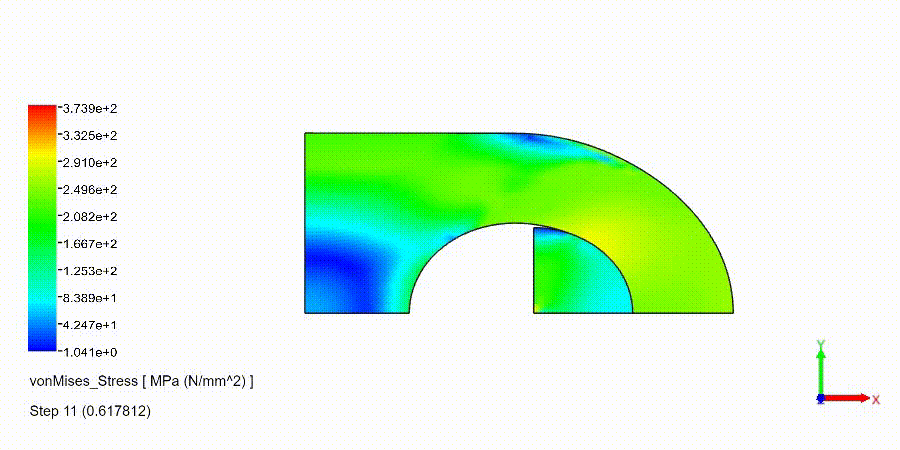
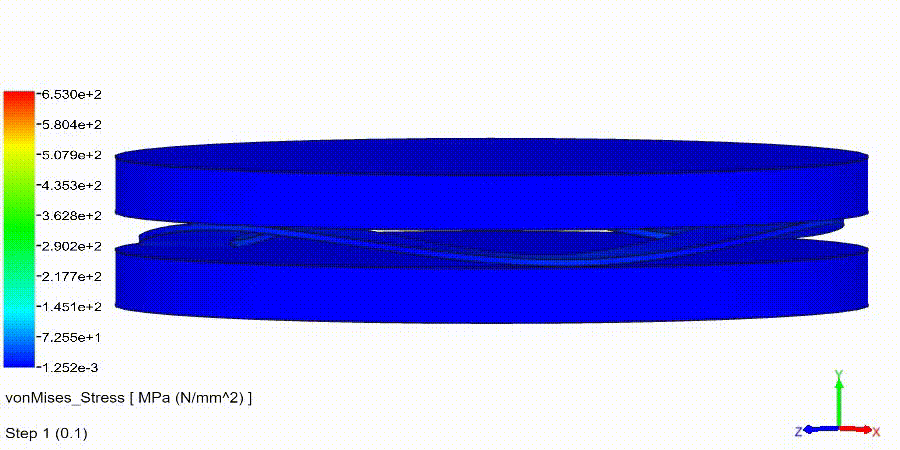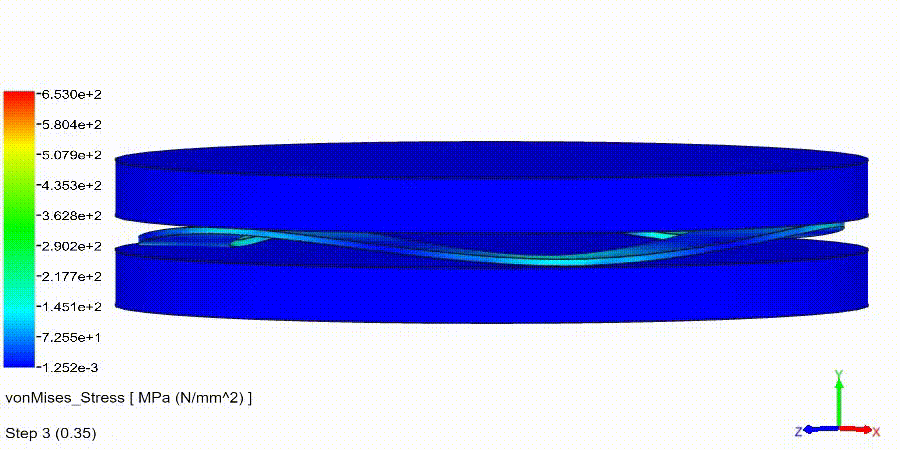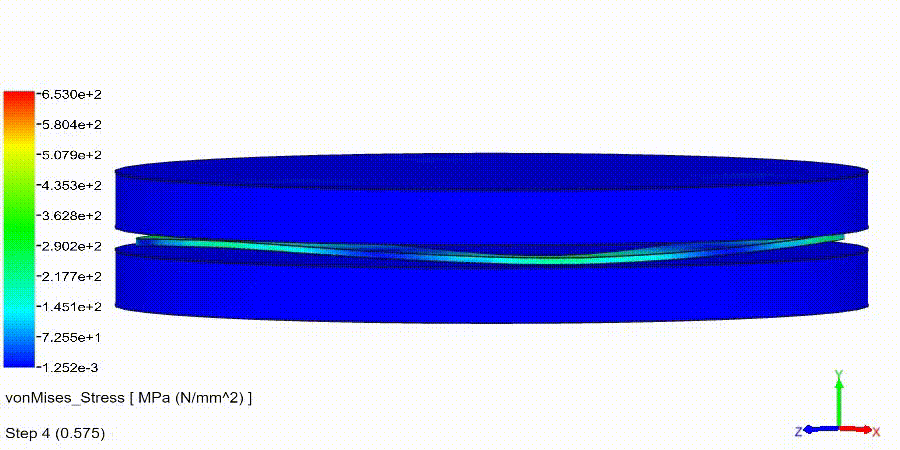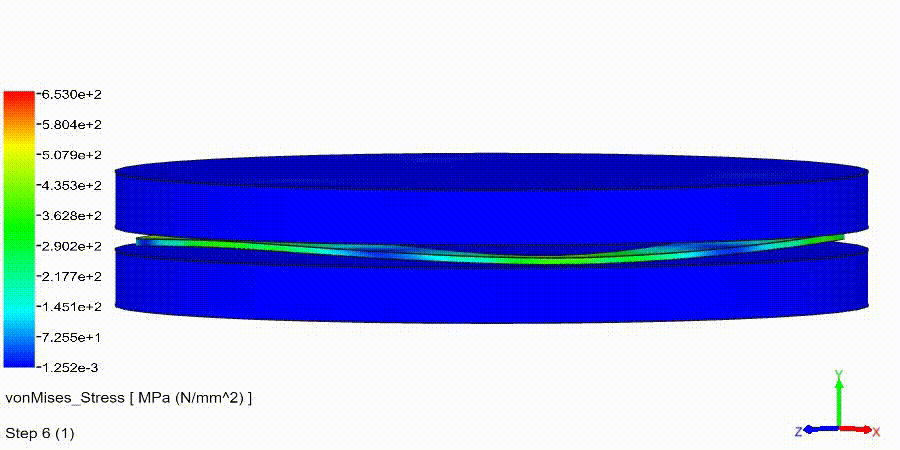
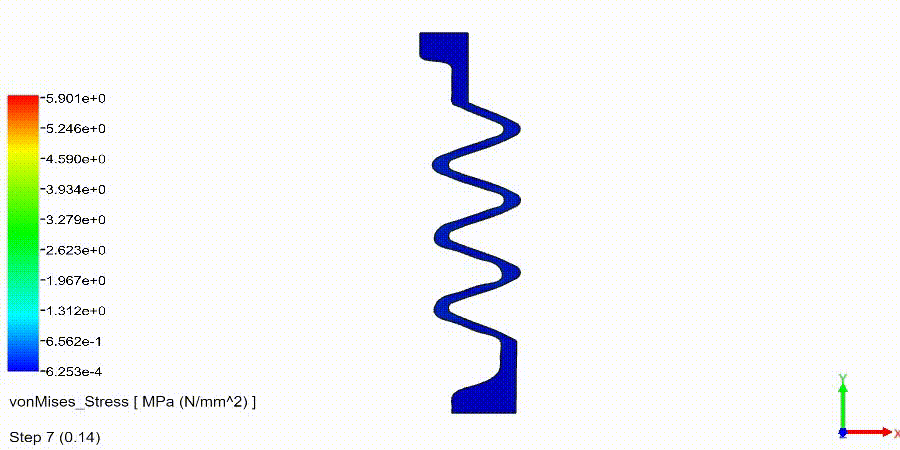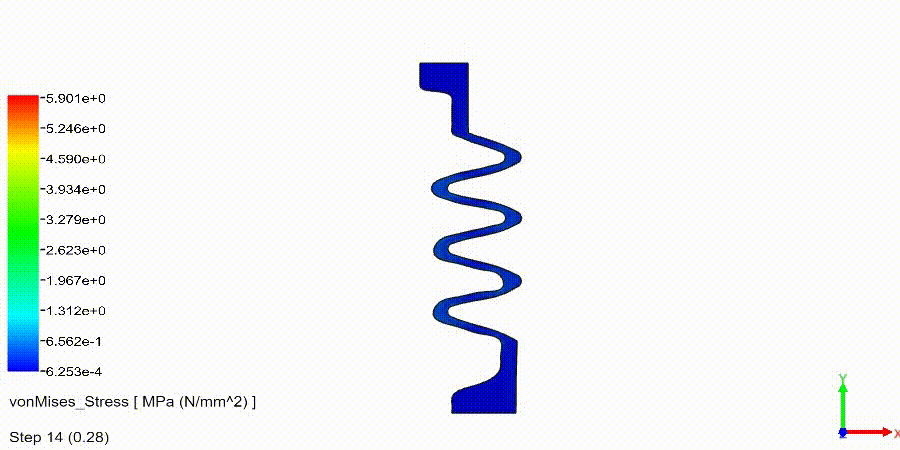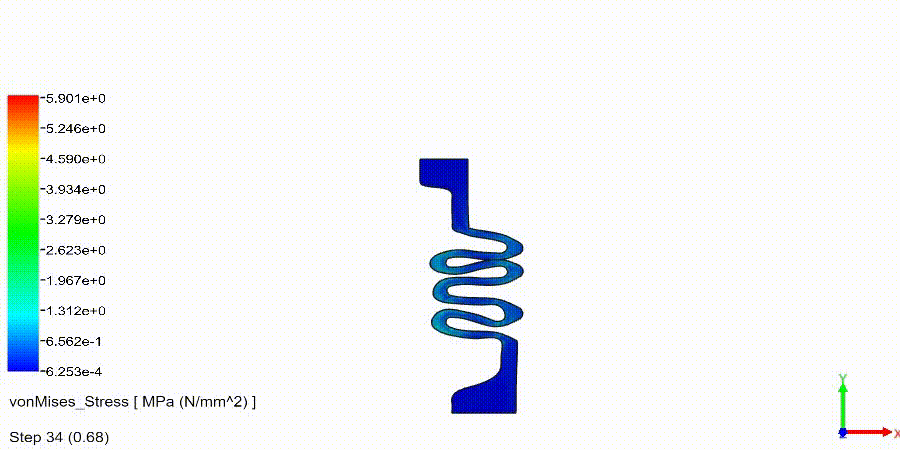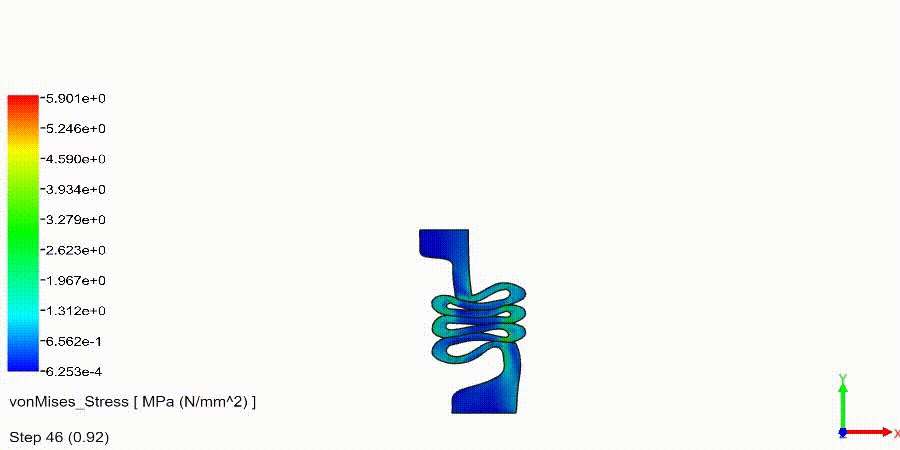
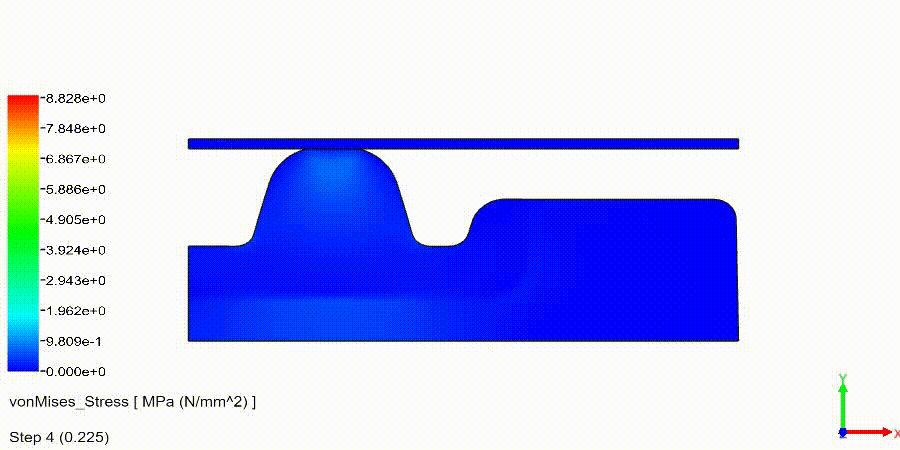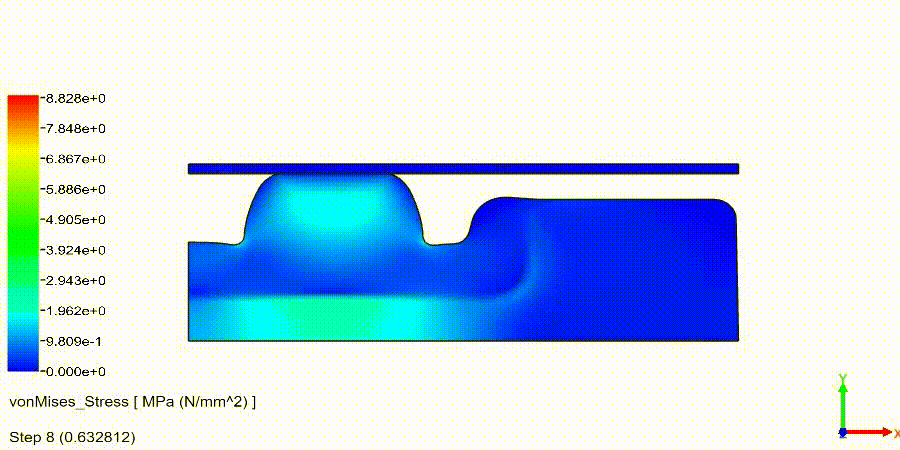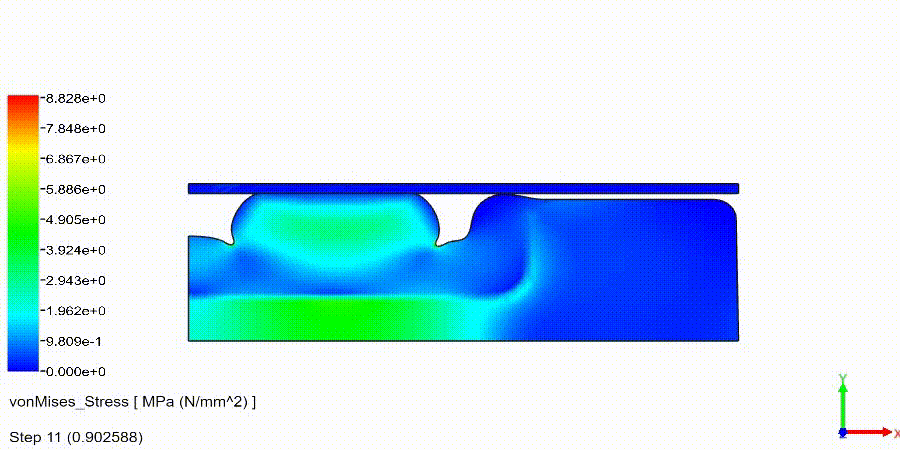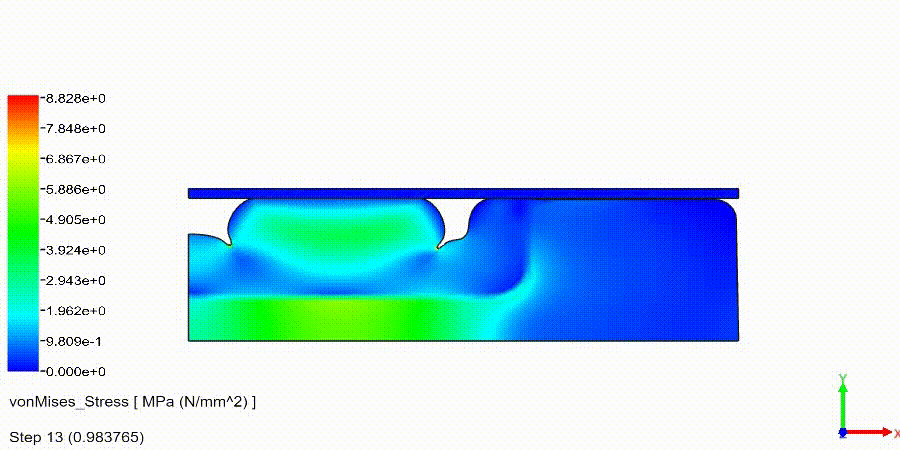
Non-Linear Static Analysis Examples:
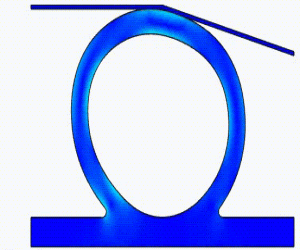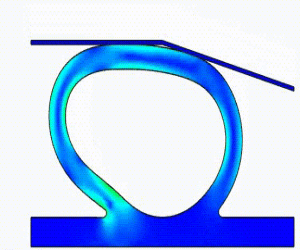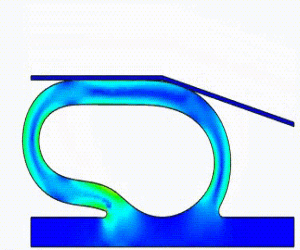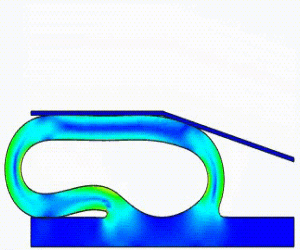
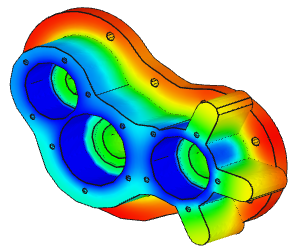
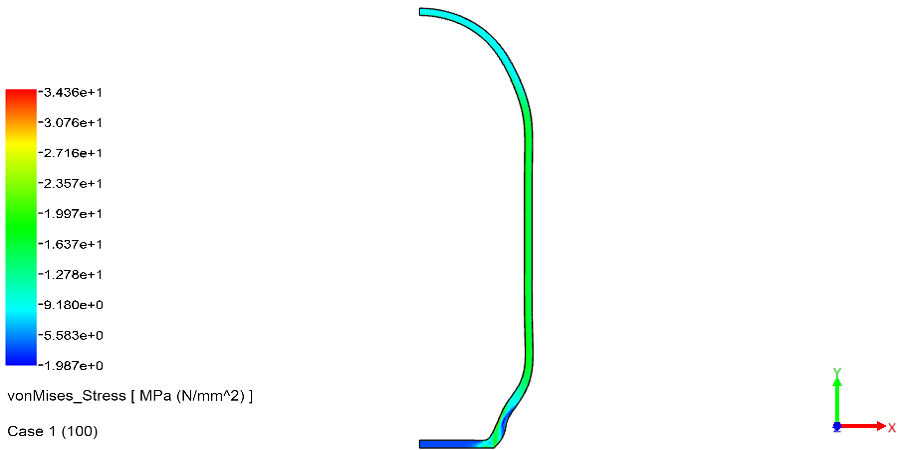
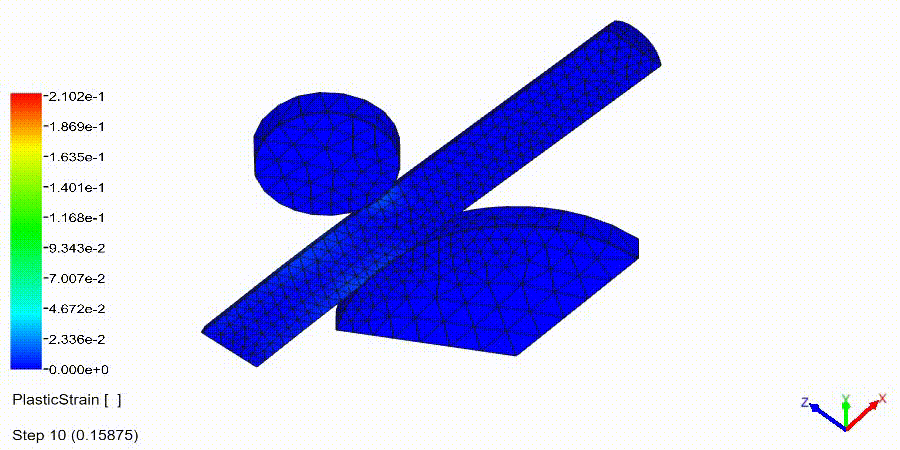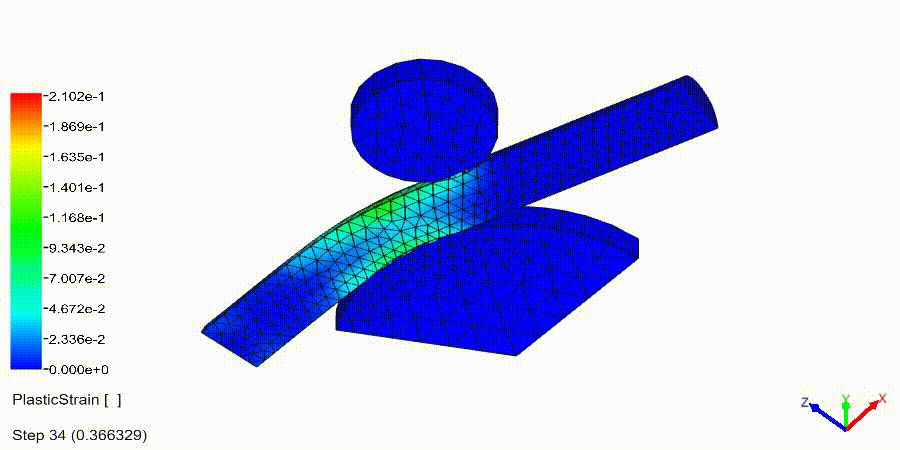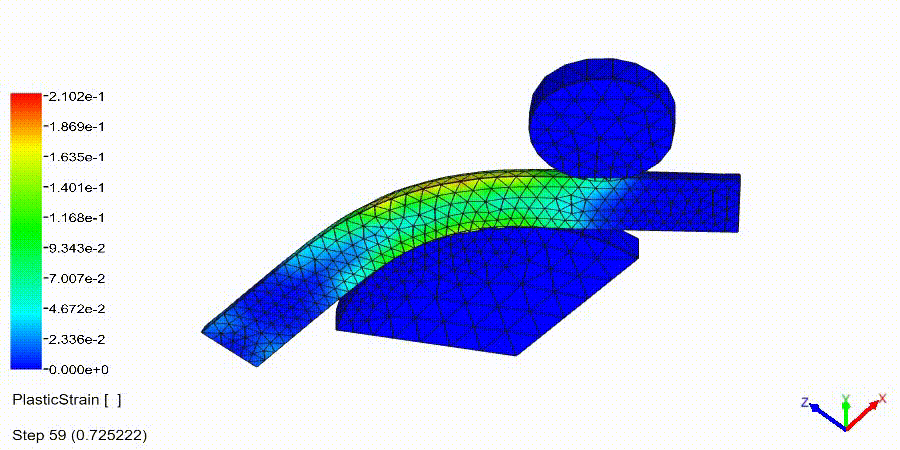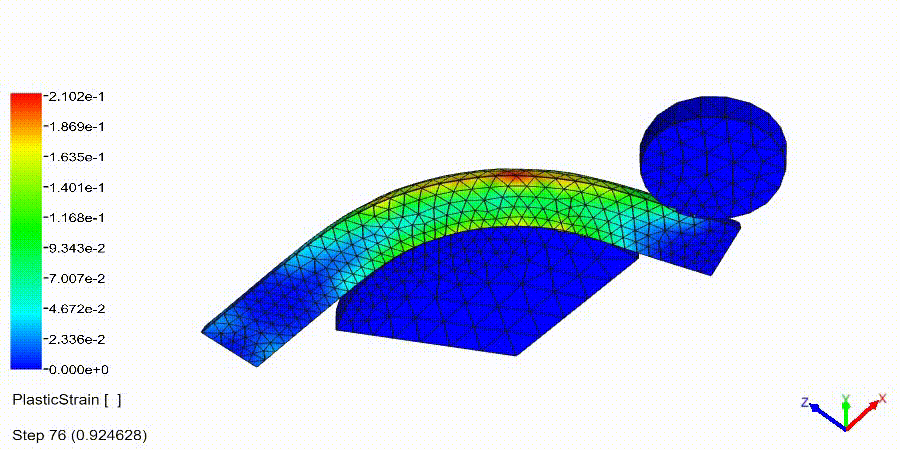
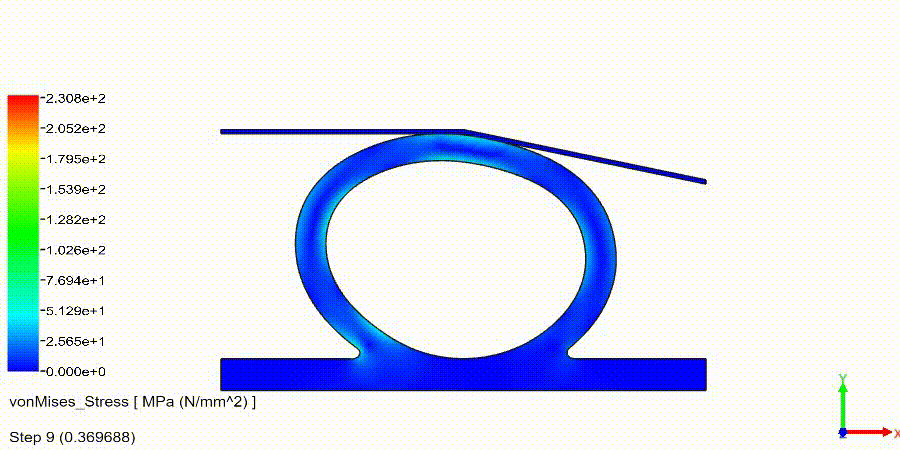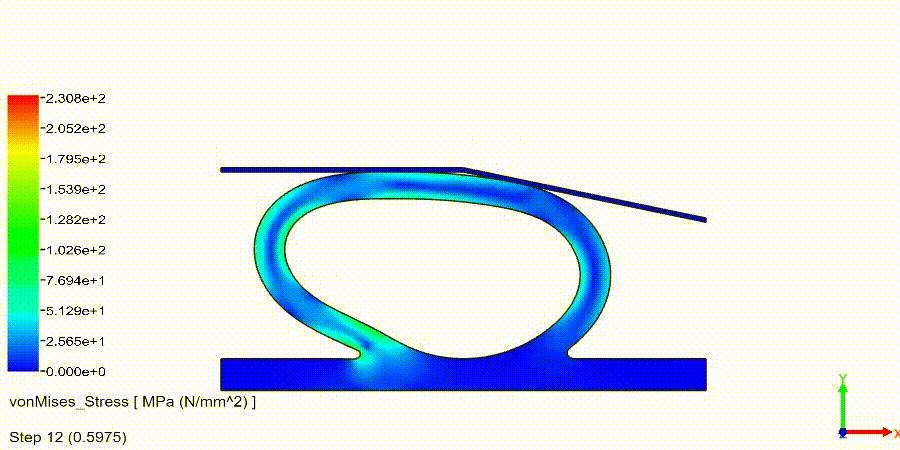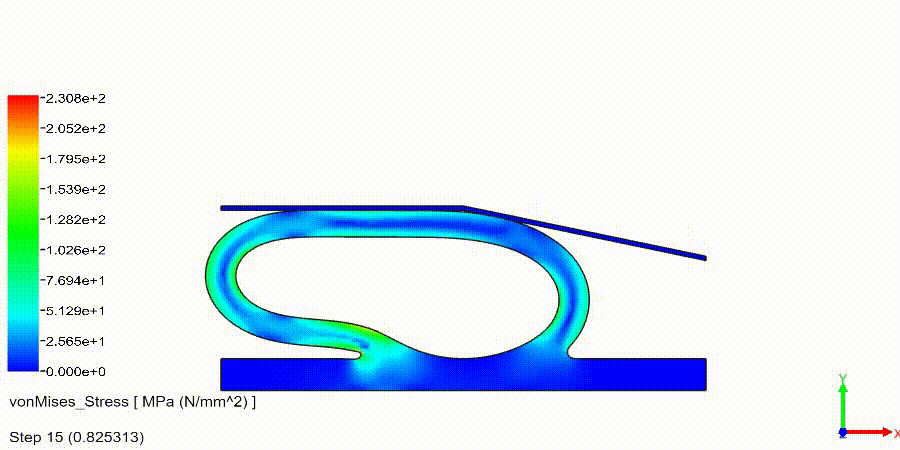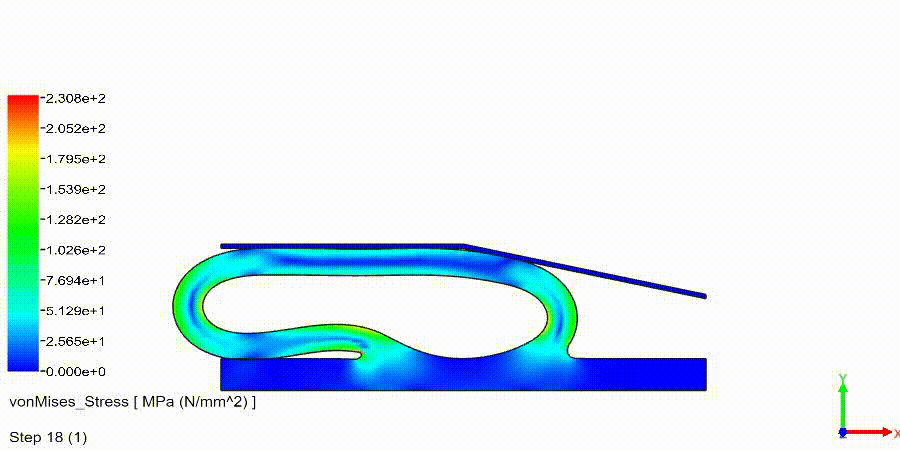
NonLinear (HyperElastic) Static Analysis Examples:
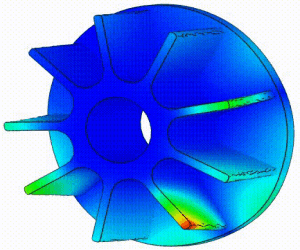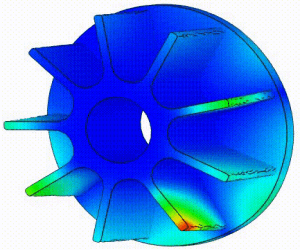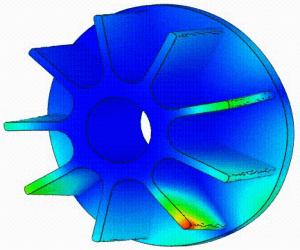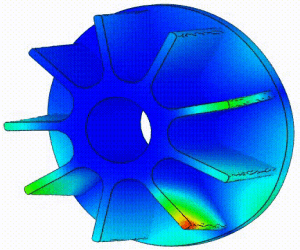
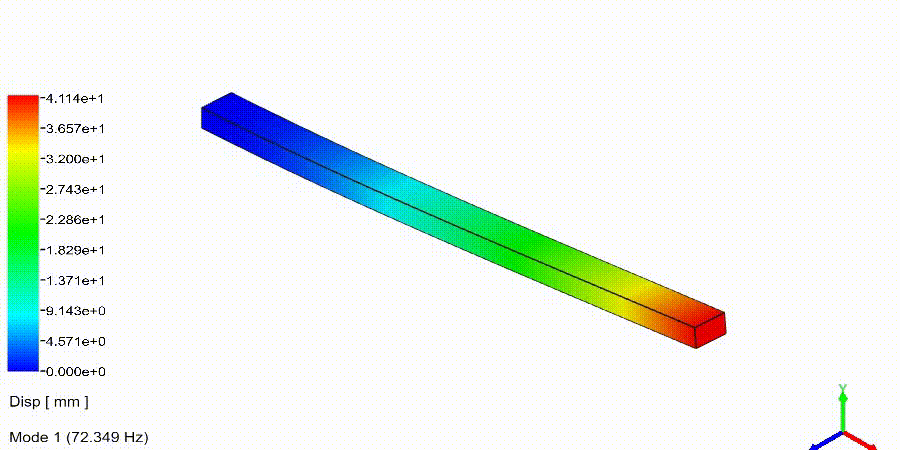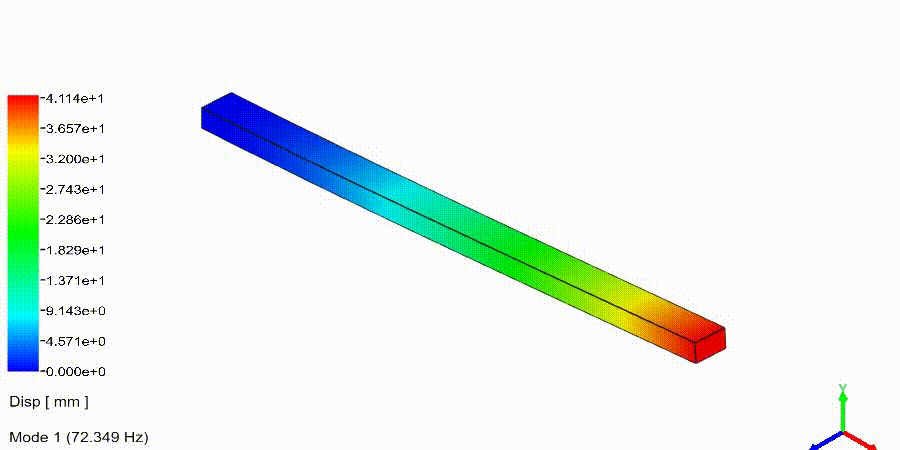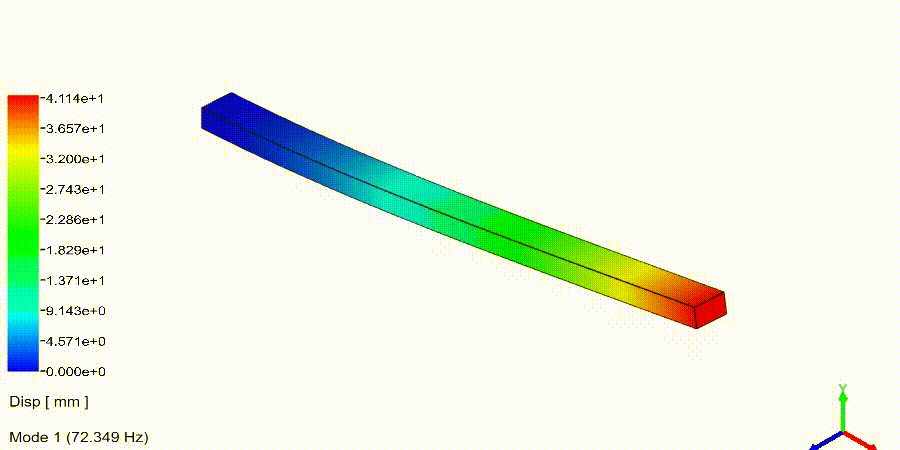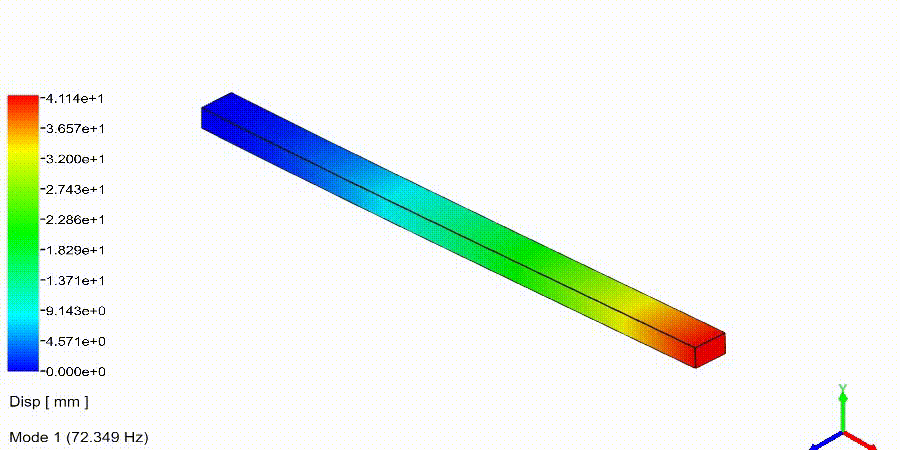
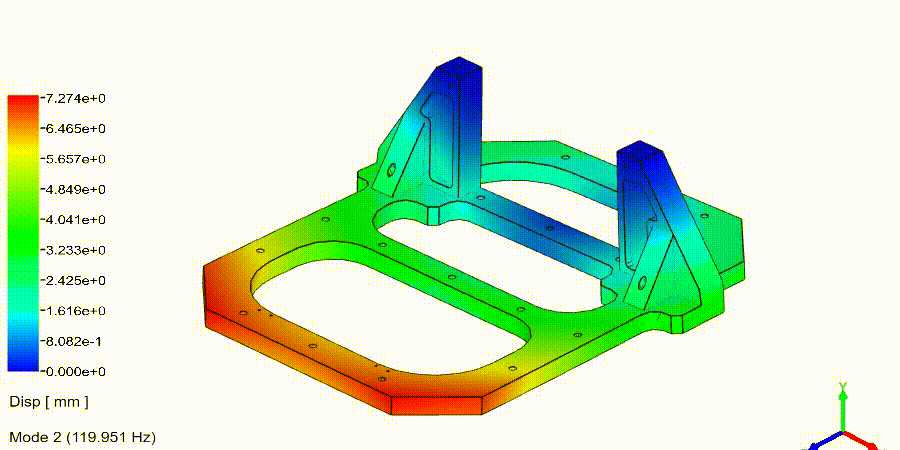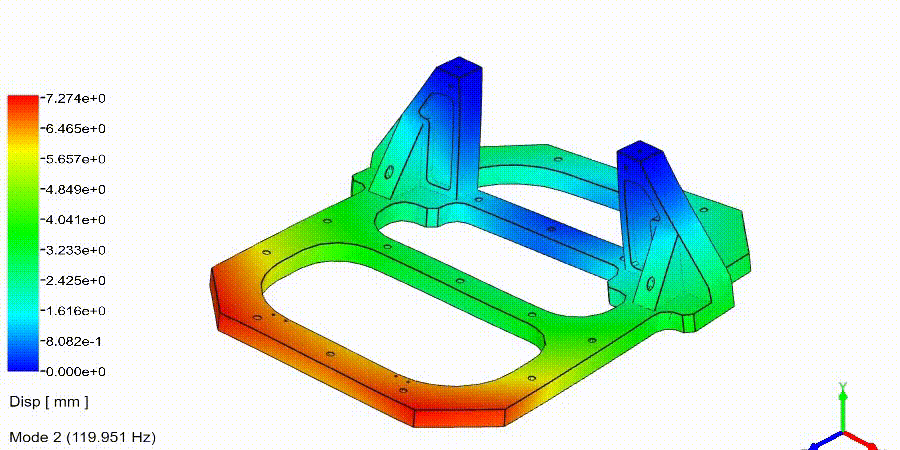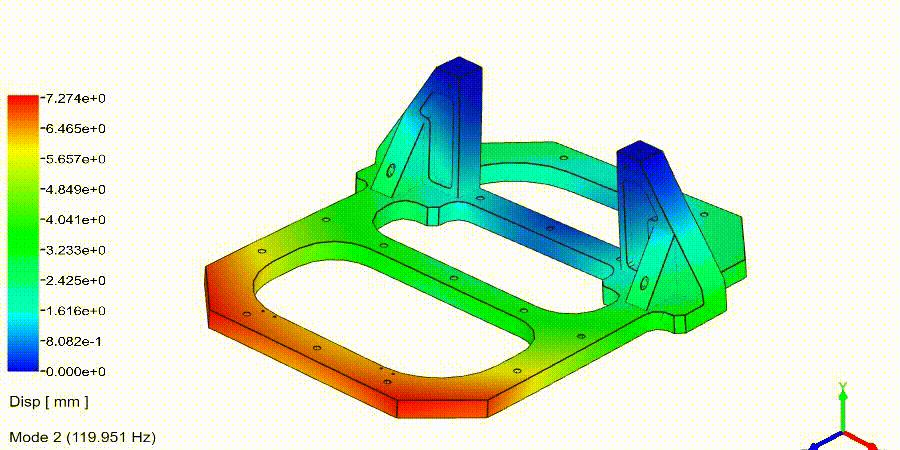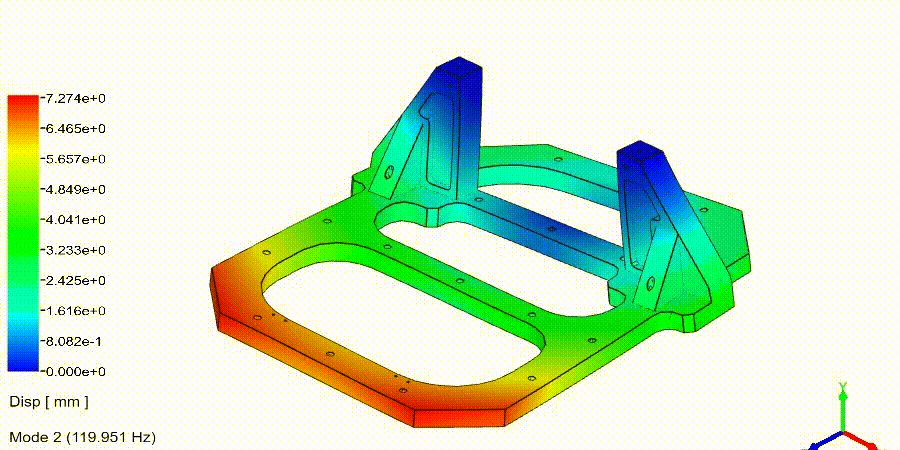
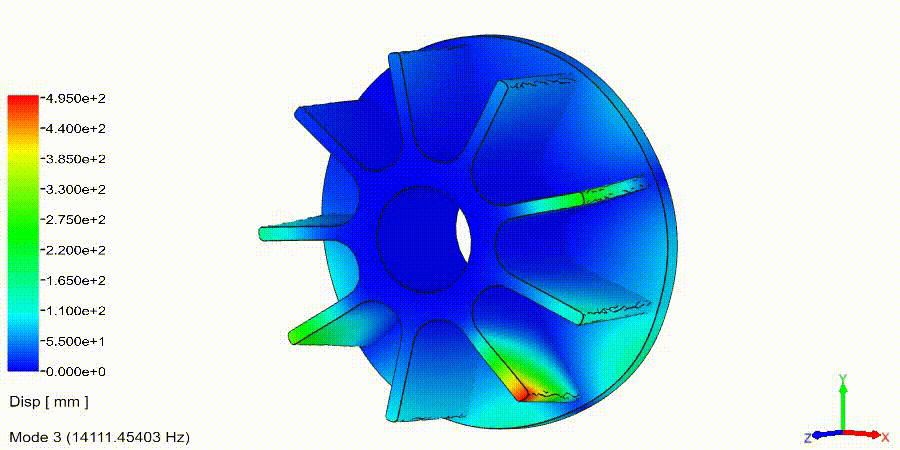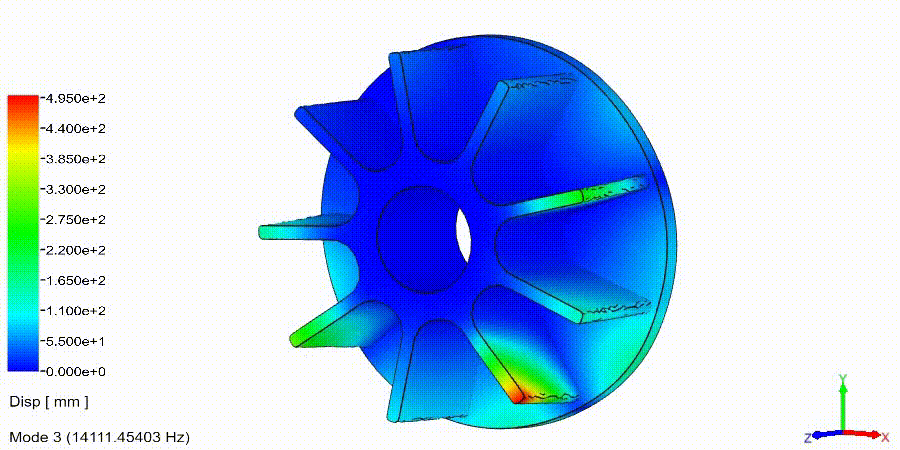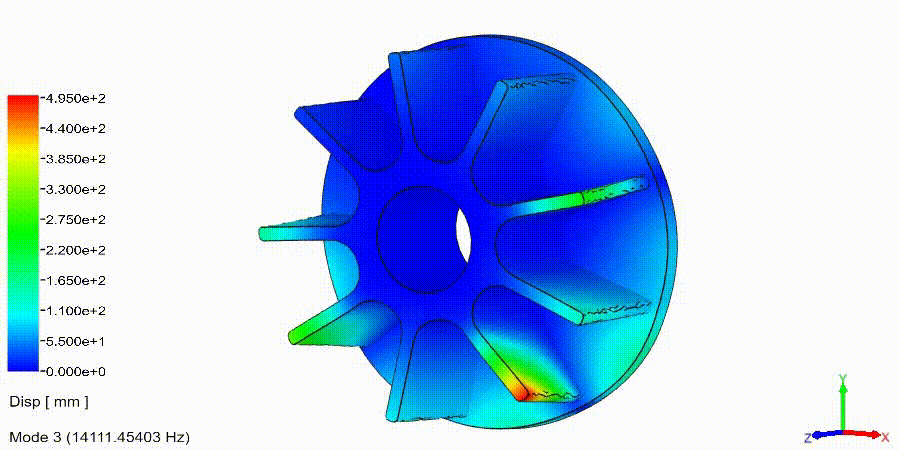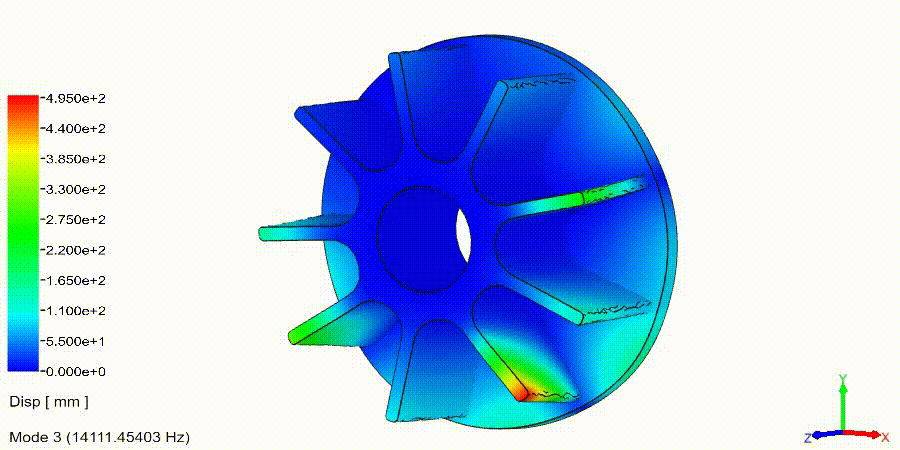
Frequency Analysis Examples:
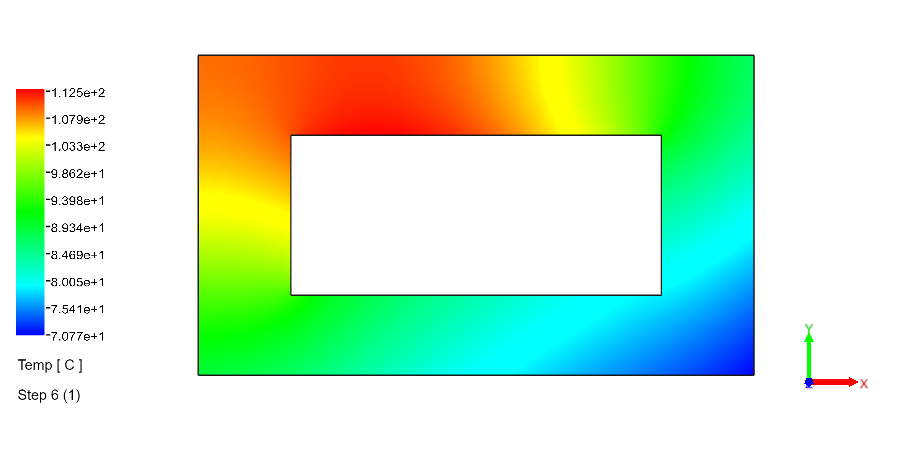
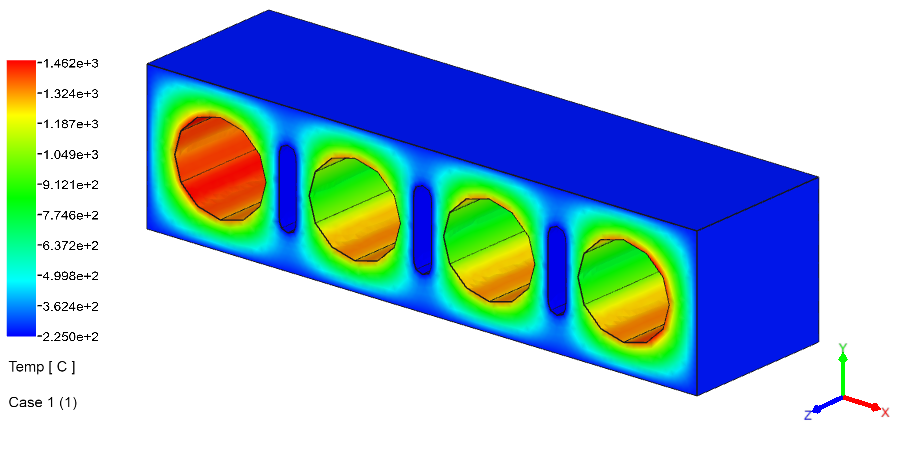
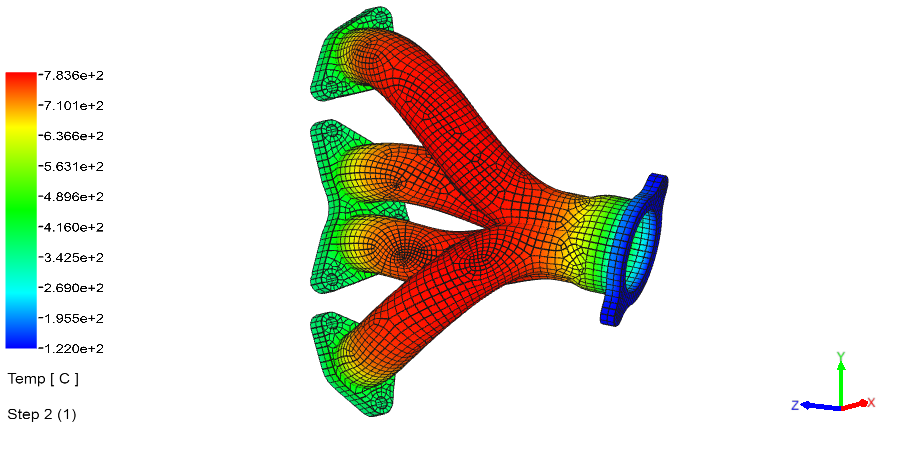
Heat Transfer Analysis Examples:
![]() Platform:
Platform:
![]() Client side Supported Web browser: MozillaFireFox, Edge, Chrome, Safari (iOS)
Client side Supported Web browser: MozillaFireFox, Edge, Chrome, Safari (iOS)![]() Operation server specification: Windows 10 Server / Linux (CentOS, Redhat, Fedora, etc.)
Operation server specification: Windows 10 Server / Linux (CentOS, Redhat, Fedora, etc.)
===> Please contact us for details Contact Us